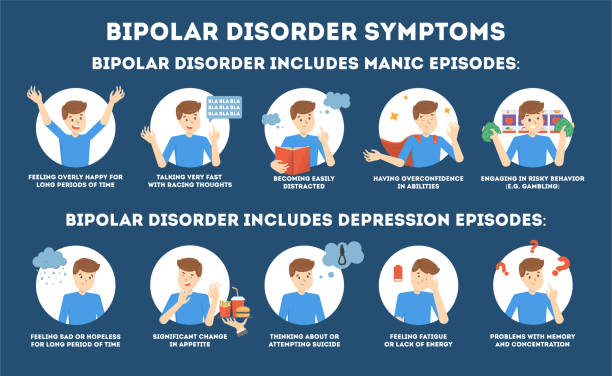
Bipolar disorder is a mental illness marked by extreme shifts in mood. Symptoms can include an extremely elevated mood called mania. They can also include episodes of depression. Bipolar disorder is also known as bipolar disease or manic depression. People with bipolar disorder may have trouble managing everyday life tasks at school or work, or maintaining relationships.
Bipolar mood disorder is a relatively common neuropsychiatric disorder with an estimated prevalence of 1% to 2%, and a high burden of disease. There is a high rate of medical comorbidity including diabetes and the metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular morbidity, and obesity, all of which are associated with inflammatory changes and oxidative stress. These comorbidities lead to a novel hypothesis that bipolar disorder is a part of a multi-system inflammatory process.
Mitochondria are necessary for the generation of energy and synaptic signaling. Mitochondrial dysfunction appears to be involved in the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder. The prevalence of the bipolar disorder in patients with mitochondrial cytopathies is higher than among healthy controls. Mitochondrial DNA deletions are increased. Mitochondrial dysfunction has thus been hypothesizing as a molecular basis of bipolar disorder. It is suggested that novel therapeutic agents for treating bipolar mood disorder should target mitochondrial function.
The generation of oxidatively generated free radicals is core to life and is normally tightly controlled. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and metabolism appear to play an important role in the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder. Not only are both total glutathione and reduced glutathione levels, which are core parts of the intrinsic anti-oxidative system decreased in bipolar disorder, but antioxidant enzyme activities are also impaired. Levels of key redox enzymes including SOD and catalase have been reported to be lower in patients with bipolar disorder. Nitrous oxide (NO) is implicated in the generation of psychotic symptoms such as delusions in bipolar disorder. A meta-analysis reported that the level of NO appears to be significantly increased in bipolar disorder. Moreover, the level of thiobarbituric acidic reactive substances (TBARS), a marker of lipid peroxidation through a reaction between free radicals and lipid structures, is increased during manic episodes and remission. This finding suggests that oxidative damage to lipid structures is probably continued during the course of bipolar disorder.
Molecular hydrogen is an odorless and tasteless gas that has the ability to rapidly diffuse through lipid membranes and enter the cell, where it easily penetrates organelles such as mitochondria as well as the nucleus. Molecular Hydrogen is an effective medication for the prevention of long-term relapse in bipolar mood disorder. Molecular Hydrogen also has effects through its impact on inflammation and by the prevention of oxidative stress and cytokine changes. These anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects are potentially neuroprotective. Molecular Hydrogen increases mitochondrial respiratory chain enzyme activities, particularly complex 1, that may be linked to its therapeutic efficacy and increases mitochondrial energy production. Molecular Hydrogen has many biological properties that make it an appealing candidate agent for a diversity of disorders sharing inflammatory, oxidative, and apoptotic mechanisms.
Call Now: 1800-102-0908
Website: www.kykindia.com